Branding and Archetypes
 As you develop your company’s brand, how do you determine what “personality” you should project? How do you know where your brand fits relative to other brands in the market? I always recommend that you do as much market research as you can. I also recommend that you study the archetypal systems developed by Carol Pearson (whose website is here).
As you develop your company’s brand, how do you determine what “personality” you should project? How do you know where your brand fits relative to other brands in the market? I always recommend that you do as much market research as you can. I also recommend that you study the archetypal systems developed by Carol Pearson (whose website is here).
Pearson is a Jungian psychologist more than a marketing maven. She has developed a set of archetypes that help people understand how to use their inner resources to enrich their lives. Fortunately for us marketing types, these archetypes can also be applied to companies and organizations. They can help you understand how you fit into a broader ecosystem and how to convey your message most effectively.
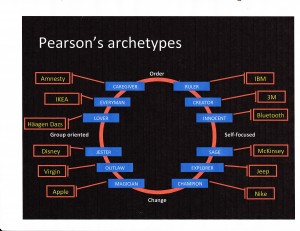
When I worked at Lawson Software, we used the simplified diagram that you see here. The diagram includes 12 basic archetypes with a company to illustrate each one.
The circle helps you understand how the archetypes fit together. For instance, note the word “Order” at the top of the circle and the word “Change” at the bottom. Simply put, the companies on the top half of the circle want to maintain the existing order, the current market structure. By comparison, the companies on the bottom half might be described as “upstarts”. They want to change — or overthrow — the current market structure.
The left and right halves of the circle also have much to tell us. The archetypes on the left side are group-oriented. Those on the right side are more self-focused. The simplest explanation is that those companies on the left of the circle focus primarily on their external constituencies. Those on the right focus more attention on internal processes and procedures.
At Lawson, we quickly decided that we were on the bottom half of the circle. We weren’t the market leaders, we didn’t dominate the segment — we needed to shake things up to find our place in the sun. Similarly, we decided that we were on the left side of the circle. We were market oriented and our mission was to make our customers stronger. In other words, we were externally focused.
So, we were on the lower left segment of the circle. We had three archetypes to choose from: 1) Jester, like Disney; 2) Outlaw, like Virgin; 3) Magician, like Apple. We then proceeded by elimination. We were a B2B company and just didn’t have the magical chops of Apple. Similarly, we weren’t a jester like Disney. Indeed, we were probably too serious.
That left us at “Outlaw”. We never really liked that label but ultimately we decided that’s who we were. (We described ourselves as “disrupters” rather than as “outlaws” but, really, what’s the difference?) To succeed, we needed to break some rules. We needed to be different and shake things up. It helped that we had a plain-spoken and charismatic CEO who was not unlike Richard Branson.
Choosing the outlaw/disrupter path almost immediately led us to use a cartoon character — very different than what you would expect from, say Oracle or SAP. With help from Fiftyeight, a very creative agency in Germany, we developed the Lars Lawson character as well as Sepp (for SAP) and ElCaro (Oracle spelled backwards). We then launched a series of video adventures on YouTube that typically garnered over a million views. (You can see the most popular videos here and here).
Did it work? You betcha. We grew faster than our segment and gained visibility globally. Bottom line: whether you’re a person or a company, it helps to know who you are and where you fit.
You can find Carol Pearson’s books here.
Make a Brand Promise or Keep a Brand Promise?

I promise.
You have $10,000 left in your marketing budget. Should you use it to make a brand promise or to keep a brand promise?
It’s a tricky question and one that Bain & Company tries to answer in a newly released white paper. (Click here). As Bain points out, we often think of branding as a way to create an emotional attachment with a consumer. Bain suggests a different approach: we create brands to shift demand. With a strong brand, we may shift demand to higher prices or greater volume or, maybe, some of both.
As we build brands, we need to make brand promises. This often involves emotional advertising and direct marketing. On the other hand, for a mature brand in an established market, more advertising may deliver diminishing returns. Rather than shifting demand, we’re just spending money in a senseless arms race.
Bain gives four examples of fashion retailers that take very different approaches to brand promises. At one end of the spectrum, American Apparel and Benetton advertise heavily and often provocatively. In other words, they’re making promises. However, recent results — stagnant at best — suggest that they’re not keeping promises.
At the other end of the spectrum, Patagonia spends far less on advertising but has invested heavily in environmental causes. Patagonia’s strong word-of-mouth momentum focuses on promises kept. Similarly, the fashion retailer, Zara, does no advertising at all. Through smart locations, however, and short, fast production runs, they’ve built a strong company. The chatter about Zara also focuses on promises kept. For both Patagonia and Zara, the results have included faster growth and higher margins than almost all their competitors.
Bain argues that brand equity is really a brand’s power to shift demand. To illustrate, the authors review brand equity for 21 different product categories. (The research is based on discrete choice analysis, which I’ll describe in more detail in the near future). The research isolates different elements of the consumer decision — allowing us to compare the power of pricing, brand, and specific features. For MP3 players, for instance, the leading brand captures 38.5% of consumer choice based on brand alone. This compares to 13.9% for the second strongest brand. In other words, the leading brand was 2.9 times more powerful than the second brand in shifting demand.
Brands were powerful in both B2C and B2B categories. Many authors have suggested that brands are not as important in B2B categories — that B2B purchase decisions are not “emotional”. The Bain study suggests otherwise. As the authors write, “Companies have built strong brands even in … B2B … categories such as construction tools and medical devices. On construction sites, the loyalty to tool brands runs as deep as the passion that fashionistas demonstrate for their favorite jeans.”
Think about your brand — whether corporate or personal. Do you need to attract attention by making more brand promises? Or do you need to build loyalty by fulfilling brand promises? Either way, consider the power you have to shift demand simply by the way you behave.
Branding: The Value of Face Time

We need some face time.
Long ago, when I was a product manager at Solbourne Computer, we were trying to answer some nagging questions about our market. We built very fast symmetric multiprocessing Unix servers — back when symmetric multi-processing (SMP) was a brave new thing. In the early going, our machines were essentially hand built and we had difficulty meeting demand. As we worked our way down the manufacturing curve, however, we learned how to build machines more quickly. It soon became clear that we could not only satisfy demand but exceed it.
So we needed more demand. To identify potential sources of demand, we studied all of our sales to date. What patterns could we identify? Unfortunately, the raw data revealed almost nothing. There were no real patterns in terms of SIC code, geography, or industry. We had sold servers to national laboratories, astronomical observatories, large companies, medium-sized companies, universities, B2B companies, B2C companies, and so on.
Since we couldn’t identify any clear patterns in the data, we decided to go out and meet our early customers. We reached out to all of our customers and requested face-to-face meetings. Ultimately, we scheduled meetings with about 50 different customers.
As we returned from our customer calls, we held lengthy meetings to discuss the results. Again, no patterns emerged. Finally, someone suggested that we simply describe our customers. Were they fat or thin? Short or tall? Old or young? Frankly, I thought that was a dumb idea but it turned out to be brilliant. As we began describing the customers, a very clear pattern emerged. First, they were all men. Second, they were in their early to mid 30s. Third, they were all heads of their department. Titles varied but they were what we would today call the CIO. Fourth, and most important, they had recently replaced a much older manager. They were new in their positions and wanted to make their mark.
Why did they buy Solbourne? We were a small company with hot new technology — symmetric multiprocessing. But we also ran on the Unix operating system — a very safe choice. Further, the benefits of SMP were well understood — the concepts were proven though the technology was new. So newly installed, youngish CIOs could use us to demonstrate that the old regime was out; a new regime was in. They could look bold without worrying too much about failure. When we figured this out, one of our pithier sales reps said, “Geez… it’s like dogs peeing on a wall. They’re using our machines to mark their territory.” All we had to do then was to figure out where the new CIOs were. But that’s a different story.
So, what’s the moral of the story? We thought we were selling very sophisticated, state-of-the-art servers. But actually, we were fulfilling a psycho/social need. We gave our buyers signaling equipment. With Solbourne servers, they could signal that they had arrived. It was a sobering lesson in selling technology. It’s often not the technology that matters but rather the (often unspoken) need the technology addresses. It’s also a lesson in the power of face-to-face meetings. If we hadn’t met our customers personally, we never would have figured it out.
Brand Names – Defense
Yesterday, I wrote about playing offense by making brand names memorable, meaningful, and likable. That’s all well and good but how do you defend a good brand name once you’ve created it? As with offense, Kevin Lane Keller and others advise you to consider three variables:
- Transferability — can you use the name for brand or line extensions? Can you transfer it to new categories, including more luxe category or more economical categories? JuicyJuice is a good name for a line of juice drinks but probably doesn’t extend to colas or
 beers. Some names don’t have much meaning in and of themselves but become so closely associated with specific categories that they can’t be extended. Starbucks, for instance, originally could apply to almost anything but now has become closely associated with coffee. Would you buy wine from Starbucks? Similarly,we perceive Volkswagen to be a reliable, economical car. When VW introduced a luxury car, they called it the Volkswagen Phaeton. By all accounts it rivaled cars that cost twice as much. But it didn’t sell well. Great car; wrong brand. By contrast, when Toyota wanted to move up market, they didn’t transfer their own name. Rather they created a new name: Lexus. Similarly, when they moved to the youth market, they created another new name: Scion.
beers. Some names don’t have much meaning in and of themselves but become so closely associated with specific categories that they can’t be extended. Starbucks, for instance, originally could apply to almost anything but now has become closely associated with coffee. Would you buy wine from Starbucks? Similarly,we perceive Volkswagen to be a reliable, economical car. When VW introduced a luxury car, they called it the Volkswagen Phaeton. By all accounts it rivaled cars that cost twice as much. But it didn’t sell well. Great car; wrong brand. By contrast, when Toyota wanted to move up market, they didn’t transfer their own name. Rather they created a new name: Lexus. Similarly, when they moved to the youth market, they created another new name: Scion. - Adaptability — can you update or freshen the name? Will it grow stale? In the early days of the office automation industry, I remember a company named Cassette Powered Typewriters. They literally added memory cassettes to typewriters to make crude word processors. As their technology improved and as typewriters fell out of fashion, the company had to change its name to CPT. Naming after a time period can also create problems. What do we do with Twentieth Century Fox?
- Protectability — can you legally protect the name? Can anyone else copy the name? Perhaps in a different category? Perhaps in a different country?
Here’s where we start to see conflict between offense and defense. An entirely original, invented name is easier to protect. But an invented name usually has no inherent meaning, no emotional associations, and low likability. You have to teach the market what the name means, always an expensive proposition. It may score high on protectability but it’s probably low on memorability, meaningfulness, and likability.
It’s virtually impossible to create a name that scores well on all six criteria. So don’t feel badly if you don’t create a “killer” name after a few brainstorming sessions. If you need to build brand equity, you should probably focus on offense. If you need to maintain brand equity, you should probably focus on defense. Figure out your brand positions and then figure out which variables to focus on. Above all, help your customers imbue the name with emotion. It doesn’t matter what you think. It only matters what they think.
(This article is based largely on Kevin Lane Keller’s book, Strategic Brand Management).
Branding: Why Do They Buy?
When I lived in Stockholm, I was responsible for customers throughout Scandinavia. One of my favorite customers was Dale of Norway, the creators of richly patterned, thick wool sweaters. The sweaters are very popular with winter sport enthusiasts in my home state of Colorado. They’re stylish and they’re practical … and therein lies a tale.
I visited Dale of Norway’s headquarters and met their CEO. The company is located in a picturesque little town called Dale. (We call it Dale as in Chip and Dale but the Norwegians pronounce it Darla). When I met the CEO I mentioned that I was from Colorado and that my wife and I were both customers. The conversation went something like this:
CEO: “Let me guess. You have one sweater and your wife has three.”
Me (surprised): “Yes. How did you know?”
CEO: “Women see our sweaters as fashion statements and they’re willing to buy more than one. Men see them as a high quality product that will last a life time. If it will last a life time, why would you ever buy more than one?”
Me: “I wish I understood my customers as well as you understand yours.”
There are a couple of lessons here. First, sometimes a satisfied customer is just that: satisfied. I was a very satisfied Dale of Norway customer. If you did a customer satisfaction survey, I would be right at the top. But I was generating exactly zero revenue for the company.
One of Dale of Norway’s challenges was to overcome the satisfied customer curse. They needed to give me (and even my wife) more reasons to buy. To complement their heavy weight sweaters, they introduced two new product lines — mid-weight sweaters and lighter weight accessories. I’m now the proud owner of a mid-weight sweater and some long underwear. I’m still satisfied but, more importantly, I’ve generated new revenues for Dale of Norway.
The second lesson: different people buy for different reasons. Don’t ever assume that what’s sauce for the goose is sauce for the gander. To the maximum extent possible, live with your customers. When you see the world through their eyes, you’ll find that different groups see your product differently. There’s nothing surprising in that — it’s just segment marketing. Unless you understand how each segment thinks, you’ll never communicate effectively with them. One message does not fit all.
The third lesson? Dale of Norway makes great sweaters, gloves, mittens, and scarves. So get out there and buy one … or two … or three. You can find them here.
